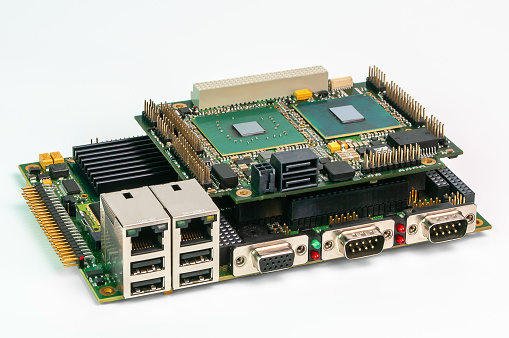
An embedded computer, as opposed to a stand-alone computer, works as part of a larger device or system. Typically, an embedded computer serves a single purpose. Embedded PC applications range from industrial automation and in-vehicle computing to digital signage, robotics, and other fields.
When you think of a computer, you probably envision a large, rectangular black box with protruding cords from the back. Vents cut into the sides of these consumer PCs allow airflow to cool the internal components. The size and design of computer systems, however, have changed dramatically as technology has advanced. Learn more on fanless embedded pc malaysia here.
Commercial embedded computers today bear little resemblance to their desktop tower counterparts. But, perhaps more importantly, the way industry employs computers has changed. Computers in the Internet of Things (IoT) are being used for things that were once thought to be impossible. But, exactly, what is an embedded PC? And how does it differ from consumer-grade tower computers in terms of form and performance?
What is an embedded system?
Embedded computer systems are referred to by a variety of names (Box PC, Gateway, Controller, Industrial PC, and so on), but an Embedded PC is essentially any specialized computer system that is put in as part of a larger device, intelligent system, or installation. Embedded computers come in an infinite variety of shapes and sizes, ranging from tiny ARM-based devices that quietly collect and relay data to all-in-one solutions that power massive earth movers and military equipment. Embedded computers also play an important role in the evolving Internet of Things, connecting machines, people, places, things, and the cloud.
How are embedded computers used?

Our embedded computers are used in everything from solar array data collection devices and navigation equipment on NASA’s planetary rovers to complex digital signage displays and modern interactive kiosks. There’s a good chance you drove right by a number of embedded computers today. You probably had no idea they were there. They silently power many of the devices and systems on which we have come to rely.
The difference between an embedded PC and a tower computer
The way an embedded PC is used is the easiest way to define it. However, there are a few key characteristics that have made embedded computers an essential component of modern system design. Embedded computers have several significant advantages over standard consumer-grade hardware. These benefits include:
- Small Form Factor: Because embedded computers are often built around small form factor motherboards such as Mini-ITX or Intel’s NUC, they can be installed in places where traditional towers would never fit. Embedded PCs can also be used in virtually any position or orientation thanks to solid state storage and flexible mounting options.
- Low Maintenance: Because embedded computers are often embedded deep within complex systems, reliability is critical. Industrial and embedded computers are designed to run continuously and without interruption. They frequently use fanless and ventless enclosures that are carefully engineered to efficiently dissipate heat. Internal components are also protected from environmental damage such as dust and airborne debris, as well as extreme temperatures and vibration.
Comments are closed, but trackbacks and pingbacks are open.